What is a Good Profit Margin? (+Industry Averages and Tips to Improve It)
What is a good profit margin, and how do you determine it? Learn everything about it here and get tips to help improve it.

You have a new business, but are you efficiently controlling your raw materials, labor, and costs?
Over the years, we have learned that one way to achieve this is to start calculating profit margins. Once you know your profit margins and why they matter, you can answer, "What is a good profit margin?"
The answer varies from industry to industry, depending on the business model, location, growth goals, and age of the business. Even major economic events can shrink margins.
Profit Margins: What are They?
Profit margins are financial metrics displayed in percentages. They help you reveal how much of your company's revenue is profit after subtracting operating costs and the costs of producing your products or services.
For example, if your business generates a 20% gross profit margin, each dollar in your revenue costs 80c to produce and sell your product, while the remaining 20c is your gross profit. To help you understand profit margins, it helps to know what each one is:
- Gross Profit Margin
- Net Profit Margin
- Operating Profit Margin
- EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortisation)
The fantastic thing about gross profit margins is that they help determine a company's profitability.
On the other hand, using the net profit margin helps you to measure your overall profitability. With the EBITDA and operating profit, you get added ways to help you evaluate how profitable your business operates.
Determining profit margins helps you assess your company's financial health. Presenting your financials helps investors, partners, stakeholders, and lenders better understand your business prospects.
Most importantly, Microapp uses our profit margins to inform our business strategies, predict income, plan for resources, and allocate our budget accordingly. You should do the same.
What is a Good Profit Margin?
A reasonable profit margin will support your business growth and continuity without needing pricing to scare away your customers. The figure can vary and depends on the business size, growth strategy, and industry.
Still, we can help generalize what a good profit margin is:
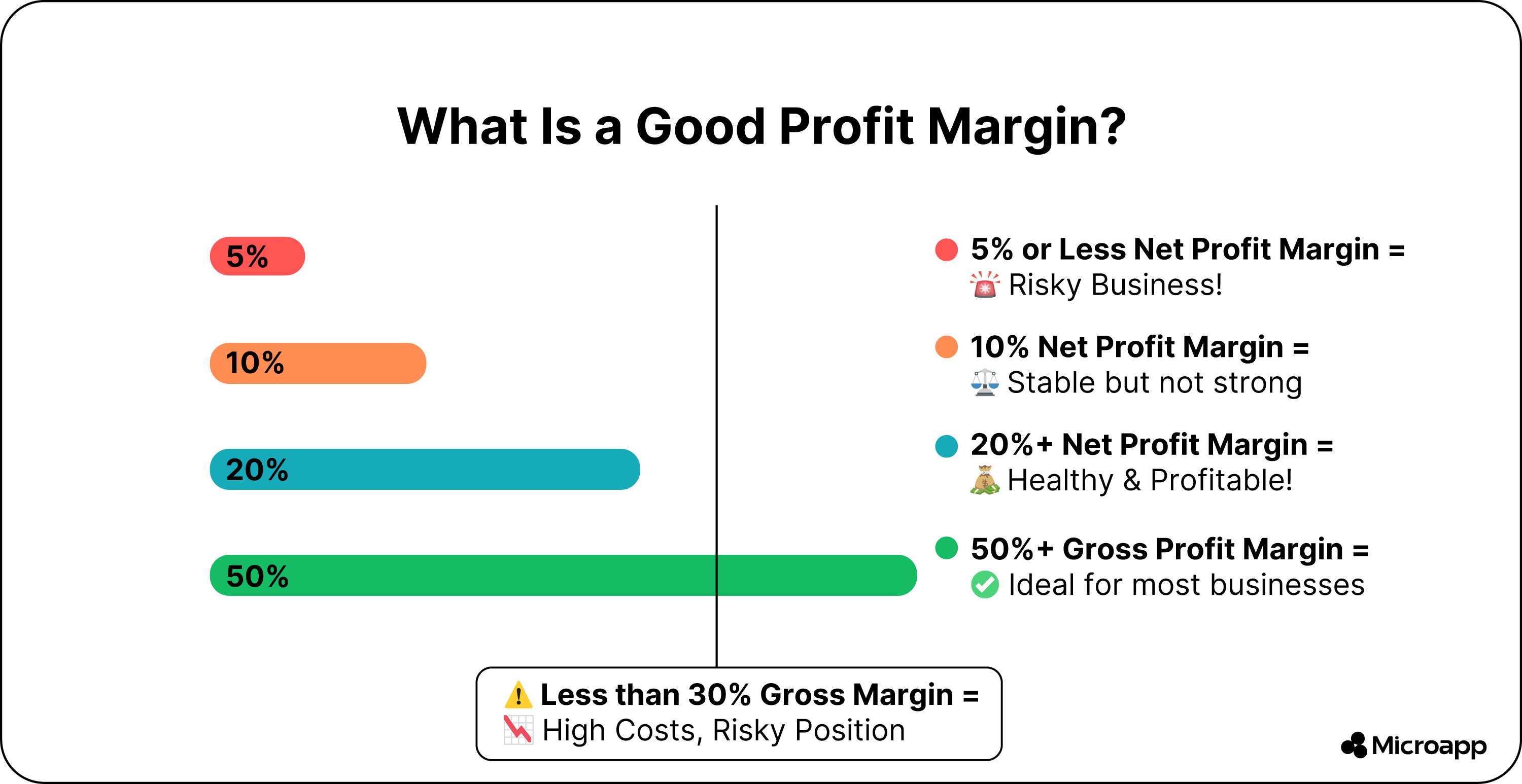
- If you have a net margin of 10%, it is considered a good profit margin for businesses.
- While a 20% or even higher means your financials are healthy.
- However, if you have a 5% net profit margin, it is low and indicates your business is in trouble.
- However, if your gross profit margin is over 50%, it is healthy for most companies.
- Furthermore, depending on the type of business and industries, they can achieve a 90% gross margin.
- Lastly, if your business has a gross margin of less than 30%, it is dangerous for your company with a high gross cost.
Still, we have found that no one-size-fits-all number can represent a good profit margin. Each business's average margin can vary, and what is a good profit margin for one may not be sustainable for the other.
High vs. Low-Profit Margins
One thing we can say when calculating profit margins in our business is that the higher the profit margins, the better.
A high profit margin allows you to manage your business costs and generate revenue. However, it can also indicate that your company needs to invest more in internal needs, such as upskilling labor, development, or research.
For example, manufacturing businesses will have a higher operating cost than retail businesses. Another company might have a high unit revenue and lower inventory turnover.
Furthermore, sector trends, economic conditions, and customer demands can affect your business's financial health. These factors must be considered before determining whether your business's profit margins are good or bad.
Profit Margin Examples by Industry
If you want to know if your profit margin is good, we found a way to determine it by comparing your percentages with those of a similar business in the industry.
Below is a table demonstrating the average profit margins of different sectors in 2025.
For more sectors to look at, explore the table here.
The table shows variances between the industry sectors' profit margins. However, the above percentages are unclear and do not help inform you about all the factors contributing to a good profit margin.
However, according to the business type, they provided a clear picture of the different relationships between profit and EBITDA.
Gross Profit Margin
The gross margin is your profit remaining after subtracting your COGS (cost of goods sold) from your net revenue. You find it as a percentage and will represent the total profit you made before deducting your overheads, administrative, and added sales costs.
So, what is a good gross profit margin? There are some levels you can consider average, low, and sound. If your gross profit ranges between 50% and 70%, it is good, and above 70% is excellent.
However, if yours is below 50%, it is undesirable. Nonetheless, lower margins are still sustainable for businesses with lower operating costs. Still, the figure remains relative and varies depending on your business model, customer trends, industry, and more.
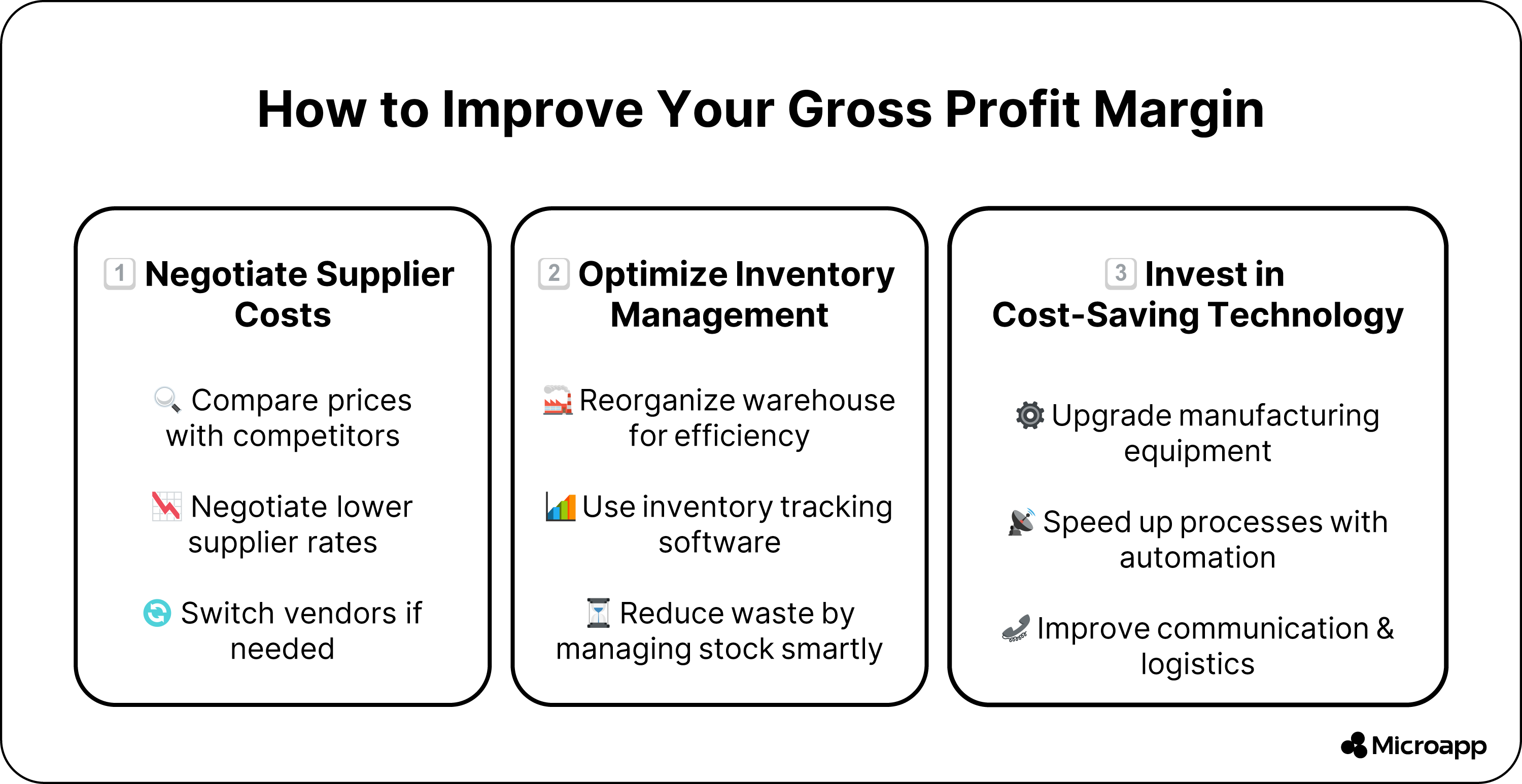
How Can You Improve Your Gross Profit Margin?
If your gross margin is below 50 percent, check your costs and income and do the following.
- Access your suppliers to see if they are still offering excellent deals. Compare their prices with those of other suppliers to help reduce your supplier costs. If your expenses are high, negotiate a better deal or switch to another vendor.
- Inventory management is a business's most significant cost, offering an excellent opportunity to reduce costs. You can save money by making small changes, optimizing your warehouse layout, or investing in inventory management software.
- Investing in better manufacturing equipment or technology can reduce product costs and improve gross margins. Also, look for ways to speed up communication, systems, and manufacturing lines.
Net Profit Margin
The net margin is the leftover profit after deducting all operating costs, such as producing products and paying taxes, from the total revenue. It is expressed as a percentage and is the most accurate representation of your business's profitability.
If your company's net profit is 10%, it is a good margin; if it is above 20%, you have a healthy business. However, if it is, it can indicate financial risk. A higher net margin means you manage your costs well to generate revenue.
Conversely, with a lower net margin, you can improve or better manage your costs and revenue structure.
How Can You Improve Your Net Profit Margin?
When improving your net margin, you must consider your tax structure to mitigate your liabilities. Based on our personal experience, we recommend contacting your accountant or a tax expert.
- We recommend seeing if you can bundle products to give your customers a better user experience. Or you can refine your overall product offer as it can boost revenue and improve the profitability of your business.
- Review your pricing strategy and consider ways to make your prices more appealing and competitive.
- Also, look at your marketing strategy to see if it is outdated and make changes as needed.
Operating Profit Margin
The operating margin is your percentage of revenue after deducting all your costs to run your business and prepare your products for sale.
You determine this by subtracting your gross revenue from your operating expenses, such as subscriptions, salaries, and rent, and the cost of goods sold.
However, an exemplary operating profit margin is between 10% and 20%. Still, it can vary from one business to another. Comparing our operating profit margin with our competitors can help us determine whether it is good.
How You Can Improve Your Operating Profit Margin
You can improve your operating margin by focusing on your operating costs.
- Examining expenditures across your business, including labor, can help you control operating costs. Look for opportunities to improve productivity, such as using automation or investing in equipment.
- Audit your processes and systems. Maintaining machinery is expensive, so optimize the process. Regular assessments can save you money in the long run.
- Also, audit your waste production and energy use. These are simple ways to reduce your operations costs.
What is a Suitable Profit Margin For Small Businesses?
In truth, these can vary and depend on your business, climate, market trends, and customers. Still, you are good if yours is over 10%, but you need to analyze your business if it is below 5%.
Yet, we found that many small businesses sacrifice their higher profit margins for increased revenue. For instance, you may reduce the sale price of a product by 10 percent to improve your total sales of the product by 20 percent.
While this is a good practice for averages, do not allow this to become your sole determinant to determine your profit margins. So, instead, if you have evidence suggesting lower margins in a growth stage, it leads to a more prominent profitability.
How Do You Calculate Profit Margins?
Each profit margin calculation formula will differ depending on the margin you want to work out. However, to work out your profit margin, you must still determine the cost of goods sold, total revenue, and operating costs.
For net margins, you must know the percentage of revenue that goes toward taxes and added costs.
Gross Margin Formula
The gross margin does not include tax costs or other expenses not included in the cost of goods sold. While it does not provide a clear picture of profitability, it helps clarify how your business generates cash from sales.
(NET REVENUE - COST OF GOODS SOLD) / NET REVENUE X 100 = GROSS PROFIT MARGIN
In the formula, your net revenue will represent the money generated from your sales. The cost of goods sold represents the direct costs that went into your production line and the preparation of the goods for sale.
Net Margin Formula
Now, if you want to determine the success of your business, the net margin gives you an accurate profitability margin.
First, you must calculate your profit, equal to your gross income minus your sales, taxes, operating costs, and interest.
Then, you insert that figure into the following formula to help calculate your net margin.
(NET PROFIT / GROSS REVENUE) X 100 = NET PROFIT MARGIN.
In this formula, gross revenue represents total sales during a specific period, while net profit is the income remaining after deducting all costs for production and selling.
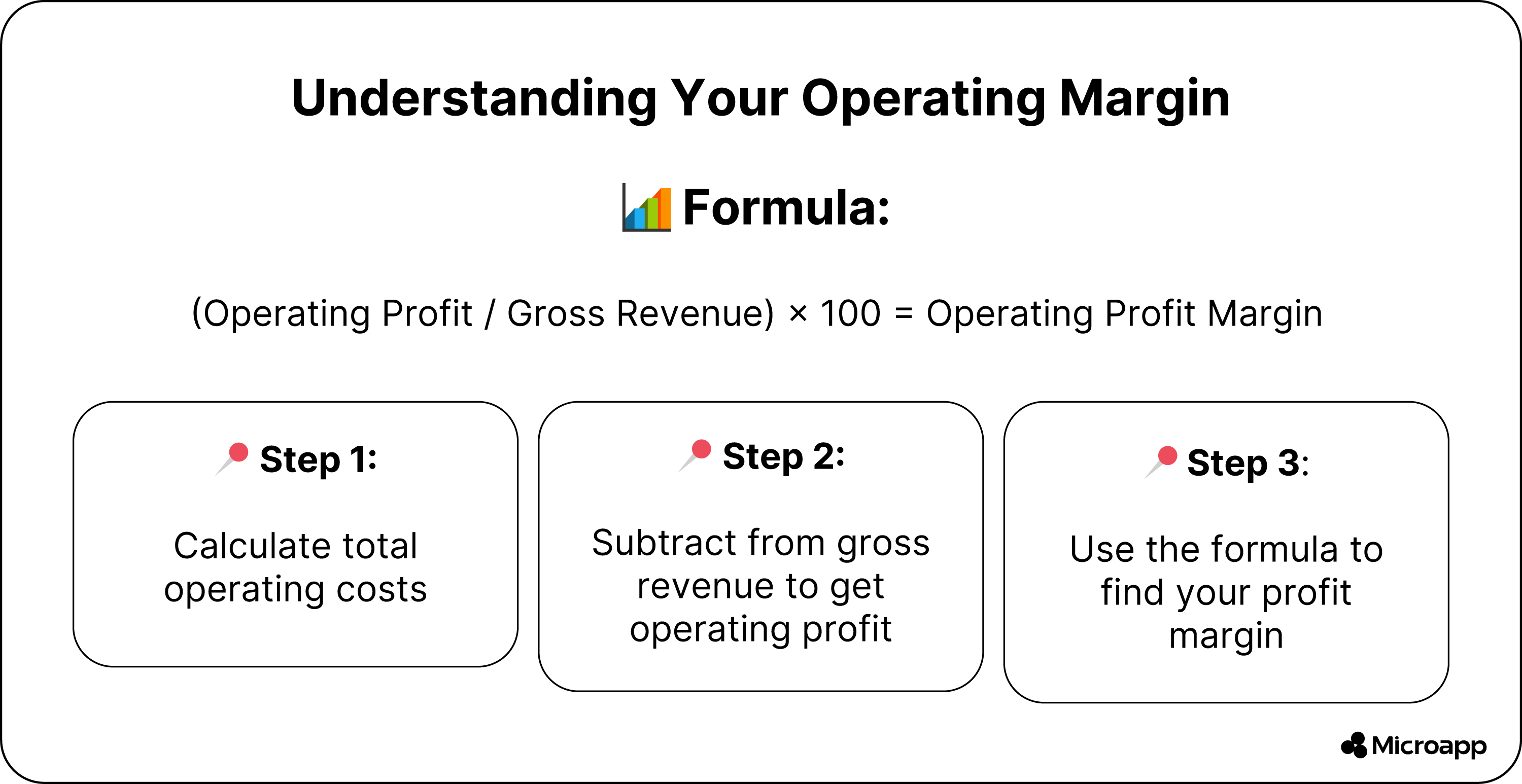
Operating Margin Formula
After deducting operating costs and revenue, the operating margin shows your profits. This metric can help you determine whether your operating costs are low or high.
Please calculate your total operating costs and subtract them from your gross margin to determine your profit. Then, add this to the formula below.
(OPERATING PROFIT / GROSS REVENUE) X 100 = OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN
After subtracting your operating costs from your gross revenue, the operating profit is the total income remaining.
How Can You Measure Your Profit Margins Accurately?
Keeping track of costs for each product or service is a lot of work. To ease your workload, invest in an inventory management system to track the average landed cost of your products with each transaction, including expenses (freight and labor). However, using our microapp tool, you can quickly determine your business's profit margin.
Wrap-Up: How Good is Your Profit Margin?
Understanding and optimizing profit margins is essential for long-term business success. Whether you analyze gross, net, or operating margins, each metric provides valuable insights into your company's financial health.
While a good profit margin varies by industry, aiming for at least a 10% net margin is a solid benchmark for most businesses. More importantly, improving your profit margin is not just about cutting costs; it is about making smarter financial decisions.
Minor adjustments, such as optimizing inventory management, refining pricing strategy, and investing in automation, can yield significant gains. At Microapp, we believe in using data to make informed decisions, and you should, too.
Use the right tools to track your financials, analyze trends, and adapt to changing market conditions. A substantial profit margin isn't just a number. It is a roadmap to sustainable growth and success.